Preventing Eye Injuries in Children
Eye injuries are the commonest cause of uniocular loss of vision. Every year, thousands of children get eye injuries requiring medical attention.

Common Causes (Agents) of Eye Injury:
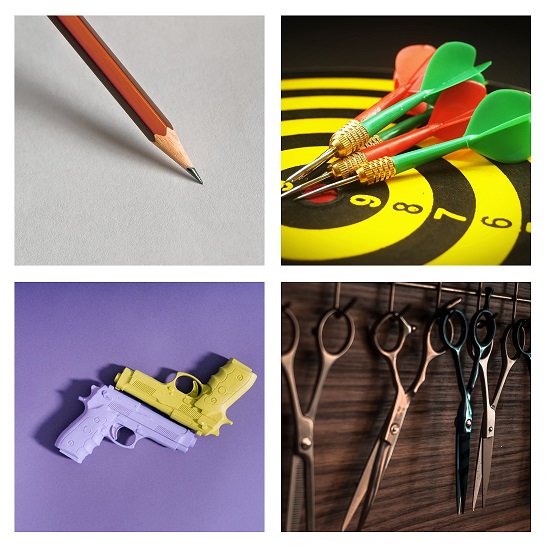
- Sharp objects including everyday objects handled regularly by children such as pencils, pens, rulers (sharp edges) and sticks. Other objects which can potentially endanger children’s eyes include scissors, nails, keys, pins and needles.
- Flying objects such as bullets from toy guns, darts and fireworks. Missiles may also be encountered with explosives especially in conflict situations.
- Heavy objects which may be thrown by children e.g. stone, shoes, balls, bags.
- A blow, punch of slap from a fist or hand or impact from a stick.
- Chemicals which may spray or pour into eyes such as with paint guns, insecticides, domestic and industrial cleaning agents.
Symptoms
- Eye pain
- Foreign body sensation
- Swollen eyelid
- Cut on eyelids
- Bleeding from between the eyelids
- Restricted eye movements
- Bulging eye
- Prolapsing dark substance from the eye
- Distorted pupils
- Loss of vision
Preventive Measures
- Caution with handling of sharp objects by children, with supervision such as with pens and pencils in the classroom; locking sharp objects away in cupboards and children should be discouraged from handling objects like pins, needles, sharp scissors, nails, knives and the likes. In addition, avoid giving children projectile toys such as pellet and BB guns, darts, bows and arrows. Children should stay far away from fireworks.
- Children should be discouraged from throwing objects at others. Heavy objects like stones, shoes, balls and such can cause considerable eye injury.
- Discourage fighting by physical means. This will greatly reduce eye injuries from blows, slaps and punches amongst children.
- Adults need to desist from hitting as a form of deterrent. This is often the cause of accidental eye injury.
- Children should wear protective eyewear for contact sports and tasks that involve flying chips of wood, metal or other substances.
- Safety gates at the top or middle of a stairway can prevent or break a fall, potentially preventing injury which may involve the eyes.
- Caution is required with house pets such as dogs, which can potentially bite a child on the face.
- Avoid front seats in a car for young children less than 12years old. Seat belts, shoulder belts and carriers for infants and toddlers should be well secured, whilst loose items within the car should be removed, as these can potentially become flying missiles in the event of a car crash.
- Keep aerosols and domestic cleaning fluids out of the reach of children to avoid accidental spray or splash into the eyes.
How to Handle Eye Injuries
- Rinse eyes thoroughly with clean water for several minutes in the event of a chemical splash or spray into eyes, and then get to an Ophthalmologist’s quickly.
- Injured eyes should be covered lightly with a clean piece of gauze or bandage and medical help sought immediately. Delay may lead to irreversible damage with potential reduction or permanent loss of vision.
- DO NOT attempt to remove sharp objects lodged in the eye or face.
- DO NOT try to forcefully prise eyelids open.
- DO NOT apply medication to injured eyes.
- DO NOT put pressure on, rub or massage injured eyes.
Eye injuries may need treatment with medication alone. However, surgery may be required to achieve best results. The Ophthalmologist makes decisions based on the individual case.